Product Grid
Diabetes
What Is Diabetes?
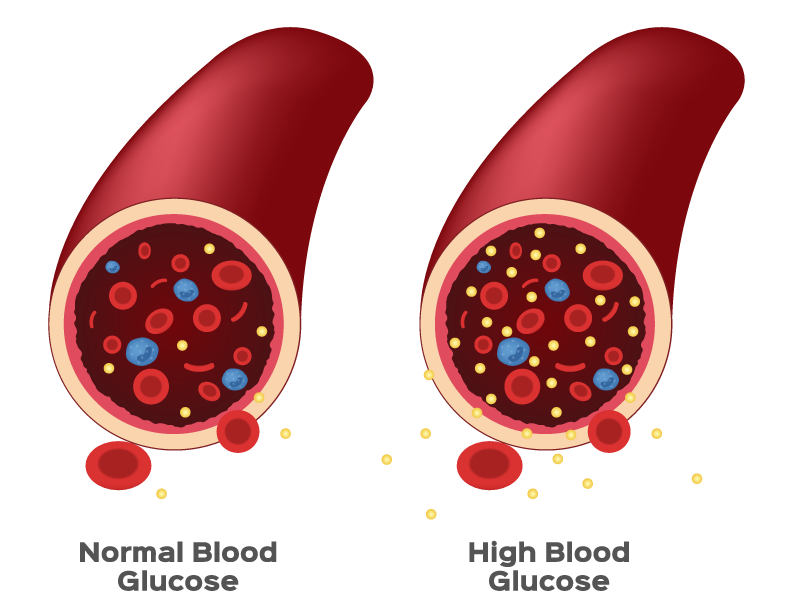
Diabetes is a form of illness associated with increased quantities of sugar present in your blood known as blood sugar. Glucose, which your body is most familiar with when it comes to energy, is manufactured by the human body or comes from the food you eat. Insulin, a hormone produced in the pancreas, helps your cells accumulate glucose from food for energy production. If you are diagnosed with diabetes, your body is no longer able to produce enough insulin, or it doesn’t use insulin properly, causing glucose not to reach your cells.
Symptoms
These symptoms may occur overnight. In type 2, the manifestations may be mild and therefore aren't noticed for many years.
Symptoms of diabetes include:
- feeling very thirsty
- having to get up to go to the toilet frequently.
- blurred vision
- feeling tired
- losing weight unintentionally
Ultimately, the prolonged diabetes may cause the arteries of heart, eyes, kidneys, and nerves to be damaged.
People with diabetes are more prone to the serious illnesses like heart attack, stroke, and kidney failure.
Diabetes can result in the loss of sight which is irreversible as it is caused by damaging the blood vessels in the eyes.
A common consequence of diabetes among many people is foot problems caused by nerve damage and poor circulation. This can bring about cases of foot ulcers and in extreme cases may eventually lead to amputation.
Types of Diabetes
Three main types of diabetes are identified: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant), all of which are forms of diabetes that have their glucose metabolism affected and lead to abnormal blood sugar levels.
Type 1 Diabetes
The cause of type 1 diabetes has been purported to be an autoimmune reaction (where the body wrongfully attacks itself), resulting in the body no longer producing insulin.
It is estimated that approximately 5%-10% of people with diabetes in the US have type 1. Type 1 diabetes can be diagnosed at any age, with the symptoms of the disease possibly starting to develop suddenly.
For those who have type 1 diabetes, insulin is the only means by which survival is possible every day. Currently, no available method of prevention for type 1 diabetes exists.
Type 2 Diabetes
In the case of type 2 diabetes, it is characterized by the body developing a resistance to insulin or not producing enough insulin, which leads to blood sugar levels not being at normal levels.
The majority of people with diabetes (around 90%) have type 2 diabetes. This condition develops over many years and is usually diagnosed in adults, but an increasing number of children, teens, and young adults are also being diagnosed.
In most cases, symptoms are not present, which makes a blood glucose test crucial for those at risk. Type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed through healthy lifestyle changes, such as:
- Losing weight.
- Eating healthy food.
- Being active.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic condition that develops in women who are pregnant and have never had diabetes before.
Pregnant women who have gestational diabetes may have the newborn at a higher risk of health issues. During most cases, gestational diabetes disappears after the baby has been born.
Contrariwise, it leads to the type 2 diabetes in your later life. The child or teen is more prone to obesity as an adult or teen and to type 2 diabetes in the future.
Causes
For diabetes understanding, it's critical to comprehend the body's typical glucose utilization.
How insulin works
The hormone insulin is manufactured in the pancreas, which is behind and below the stomach.
- Insulin is discharged into the bloodstream by the pancreas.
- The insulin circulates, so the sugar comes inside the cells.
- Insulin is the main regulator of fats and sugars in the blood.
- When the blood sugar level reaches the low point the insulin release from the pancreas also drops.
The role of glucose
Glucose, a type of sugar, is an energetic source for the cells that consist of muscles and other tissues.
- Glucose comes from two major sources: food and the liver which are the main sources of cholesterol.
- Sugar is absorbed into the blood vessels where insulin assists in transporting it inside the cells.
- The liver is the place where glucose is stored and later it becomes.
- If glucose levels are low, like when you haven’t eaten for some time, the liver releases glycogen stored in it and turns it into glucose. It helps prevent a decrease or increase in blood sugar levels.
What the specific reason for most diabetes types is no one knows. Regardless of the mechanism, sugar accumulates in the bloodstream in all cases. It is the same due to lack of production of insulin by the pancreas.
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes may have a multifactorial origin, with gene or environmental factors contributing to the development of the disease. It is unclear what the role of those factors could be.
Precautions
There is a need to look at the specifications for every machine in every case, as machines will vary. However, the following precautions and steps generally apply to many devices on the market
- Make sure you wash and dry your both hands before touching the test strips or meter.
- To ensure you get the desired result, do not use the test strip more than once. Keep the strips in their original canister to avoid moisture from outside coming in contact with the strips and eventually changing its result.
- Always keep canisters closed after use.
- Before using, check the data of the expiration date.
- Verifying the necessity of coding the machine prior to use, while this may be the case with older models.
- Keep them in a cool and dry place.
- Bring the device and test strips to your doctor's office visits so medical personnel could test their efficacy.
SUGGESTION FORM
PRODUCT REQUEST FORM


px(4).jpg.webp)
px(5).jpg.webp)


px.jpg.webp)


